Plastics Available In 3D Printing Service
Our 3D printing service offers a wide range of plastics, including PLA, ABS, PETG, Nylon, Polycarbonate, TPU, Resin, PEEK, ASA, PMMA, ULTEM, and HIPS, ensuring durable, flexible, and high-performance parts tailored to diverse industrial and functional needs.
Send us your designs and specifications for a free quotation
All uploaded files are secure and confidential
Plastics 3D Printing Technologies
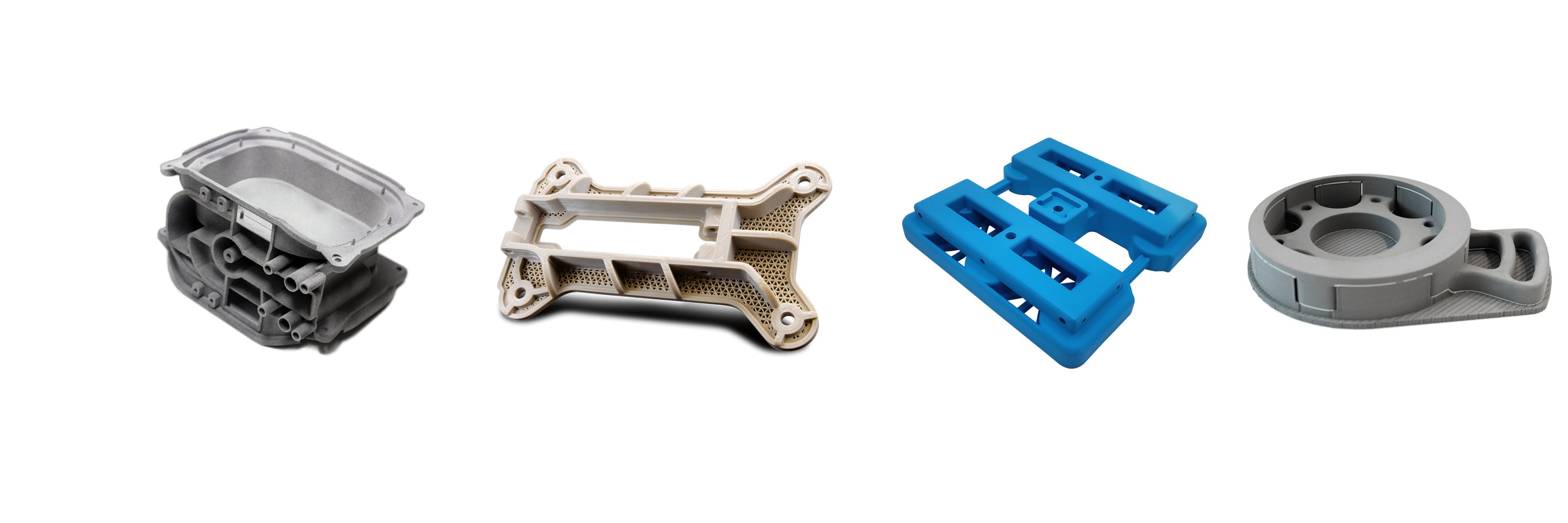
Plastics 3D Printing Technologies, including FDM, FFF, SLS, and PolyJet, offer versatile, cost-effective solutions for creating durable, functional parts. These methods support a wide range of materials, ideal for prototyping, complex geometries, multi-material components, and high-resolution prints.
Typical Plastic Used In 3D Printing
Plastics used in 3D printing provide versatility, affordability, and durability for various industries, including prototyping, medical, and consumer products. Common types include PLA for eco-friendly applications, ABS for strength and heat resistance, PETG for impact resistance, Nylon for flexibility and toughness, and PEEK for high-performance aerospace and medical uses. These materials enable precise, functional, and customized 3D-printed parts.
Let's Start A New Project Today
How To Choose The Right 3D Printing Plastics
Choosing the right 3D printing plastic depends on your project’s needs. PLA is great for ease-of-use and prototyping, while ABS and PETG deliver durability for functional parts. For higher performance, Nylon, PC, TPU, and specialty materials like PEEK, ASA, PMMA, and ULTEM offer enhanced mechanical and thermal properties. Consider printability, strength, heat resistance, and finish quality to select the best plastic for your application.




