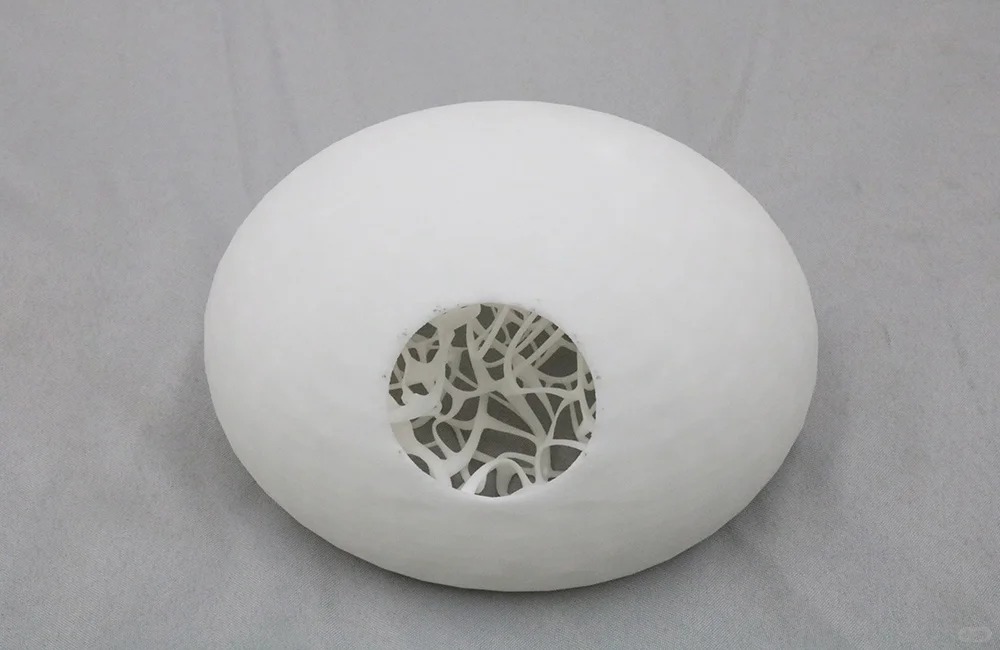
Transforming Ideas into Reality: Custom Plastic 3D Printing Across Industries
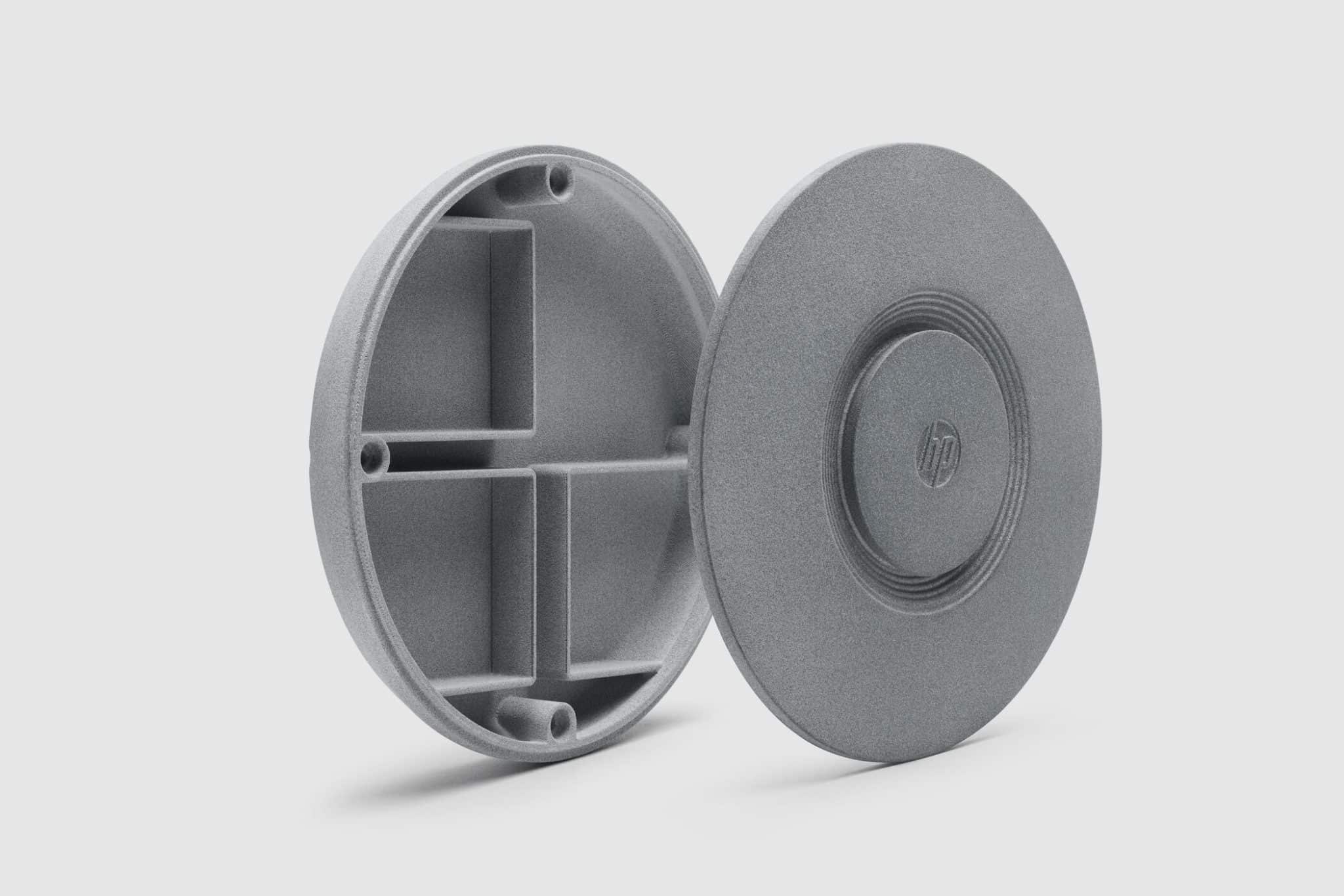 In the ever-evolving world of additive manufacturing, custom plastic 3D printing has become an invaluable tool for creating prototypes, functional parts, and end-use products. With its ability to produce intricate designs and complex geometries with high precision, plastic 3D printing is rapidly transforming industries ranging from aerospace to healthcare. Whether it's for rapid prototyping or small-scale production runs, custom plastic 3D printing offers flexibility and versatility like no other manufacturing method.
In the ever-evolving world of additive manufacturing, custom plastic 3D printing has become an invaluable tool for creating prototypes, functional parts, and end-use products. With its ability to produce intricate designs and complex geometries with high precision, plastic 3D printing is rapidly transforming industries ranging from aerospace to healthcare. Whether it's for rapid prototyping or small-scale production runs, custom plastic 3D printing offers flexibility and versatility like no other manufacturing method.
This blog explores the various plastic 3D printing technologies, the materials available, and how this transformative technology is being used across multiple industries to bring innovative ideas to life.
Plastic 3D Printing Technologies: A Gateway to Innovation
Plastic 3D printing encompasses several technologies, each with advantages depending on the project's specific requirements. Some of the most popular 3D printing technologies for plastic parts include:
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): One of the most widely used technologies, FDM extrudes heated plastic filament through a nozzle to build up layers. It’s perfect for prototypes, tooling, and low-volume production runs. Commonly used materials include PLA, ABS, and PETG.
Stereolithography (SLA): SLA uses a laser to cure liquid resin, creating highly detailed and smooth parts. SLA is known for producing parts with excellent surface finish and fine details, making it ideal for jewelry, dental, and medical industries.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS uses a laser to sinter powdered plastic into solid parts, offering greater strength and durability than FDM. SLS parts are suitable for functional prototypes and end-use parts, particularly in industries such as aerospace and automotive.
Multi Jet Fusion (MJF): This advanced 3D printing method uses a fusing agent to bond layers of nylon powder. MJF allows for high throughput, excellent mechanical properties, and fine detail, making it ideal for producing complex, high-performance parts for automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial applications.
Each of these technologies allows for creating highly accurate and functional plastic parts, offering a level of customization that is difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
Types of Plastic Materials in 3D Printing
One of the major benefits of custom plastic 3D printing is the vast range of materials available, each offering unique characteristics tailored to specific applications. Below are some of the most commonly used plastic materials in 3D printing:
Material | Applications | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
Prototyping, consumer products | Biodegradable, easy to print, low warping | |
Functional prototypes, automotive parts | High strength, impact resistance, heat resistance | |
Functional parts, food packaging, medical devices | High strength, chemical resistance, ease of printing | |
Wearable parts, automotive, robotics | Durability, flexibility, abrasion resistance | |
Industrial parts, high-strength functional prototypes | High impact resistance, heat resistance, optical clarity | |
Flexible parts, gaskets, seals, footwear | Elasticity, wear resistance, flexibility | |
Aerospace, automotive, industrial machinery | Heat resistance up to 250°C (482°F), strength under load | |
Dental products, crowns, bridges, surgical guides | Biocompatibility, high precision for dental applications |
Each material offers distinct benefits, making it suitable for different applications depending on the mechanical properties required for the part. Whether for low-cost prototyping with PLA or high-strength, durable parts with Nylon or Polycarbonate, there’s a plastic material suited to every need.
Applications of Custom Plastic 3D Printing Across Industries
Plastic 3D printing has seen widespread adoption across various industries due to its ability to produce highly customized parts quickly and cost-effectively. Below are some key industries benefiting from custom plastic 3D printing:
Aerospace and Aviation: The need for lightweight, durable components is crucial in the aerospace industry. Plastic 3D printing produces functional prototypes, brackets, tools, and custom fixtures. The high strength-to-weight ratio of materials like Nylon and Polycarbonate makes them ideal for these applications.
Automotive: In automotive manufacturing, plastic 3D printing is used for creating prototype parts, custom tools, and even end-use parts for vehicles. ABS and PETG are common materials used to produce automotive components that require impact resistance and durability.
Healthcare: The healthcare sector benefits significantly from custom plastic 3D printing, with medical devices, prosthetics, orthotics, and surgical guides being produced with materials like PLA and high-temperature resins. The ability to print precise, patient-specific parts has revolutionized the way medical devices are manufactured.
Consumer Electronics: Plastic 3D printing is widely used in the consumer electronics industry for producing enclosures, functional prototypes, and parts for products like smartphones, wearables, and home appliances. Materials such as ABS and Polycarbonate are commonly used for these applications due to their durability and resistance to high temperatures.
Fashion and Jewelry: Custom plastic 3D printing allows designers in the fashion and jewelry industries to create intricate designs easily. Using materials like SLA resins, designers can produce highly detailed jewelry prototypes that can later be cast into metal.
Education and Research: In educational settings, plastic 3D printing allows for creating custom educational models, research prototypes, and interactive teaching aids. Materials like PLA are commonly used due to their low cost and ease of use, making them ideal for classroom and laboratory environments.
Benefits of Custom Plastic 3D Printing
Custom plastic 3D printing offers several advantages over traditional manufacturing methods:
Design Freedom: 3D printing creates complex geometries and designs that would be impossible to achieve with conventional manufacturing processes.
Rapid Prototyping: Designers and engineers can quickly iterate on designs, reducing the time required to bring new products to market.
Low-Volume Production: Plastic 3D printing is cost-effective for small production runs, allowing for the production of highly customized parts without the need for expensive tooling or molds.
Reduced Waste: Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, 3D printing only uses the material required to create the part, reducing material waste.
Why Choose Custom Plastic 3D Printing?
Custom plastic 3D printing provides unmatched flexibility, precision, and speed for industries that demand high-quality, customized components. Whether you're in the aerospace, automotive, healthcare, or consumer electronics industry, this technology enables the creation of functional prototypes, low-volume production runs, and highly specialized parts tailored to your specific needs. By choosing custom plastic 3D printing, you can unlock new possibilities in design, reduce time-to-market, and create innovative solutions that drive your business forward.
FAQs
What are the main types of plastic used in 3D printing?
How does FDM 3D printing differ from SLA and SLS?
What industries benefit most from custom plastic 3D printing?
What are the advantages of using plastic 3D printing for low-volume production?
How do plastic 3D printed parts compare to traditionally manufactured parts in strength and durability?